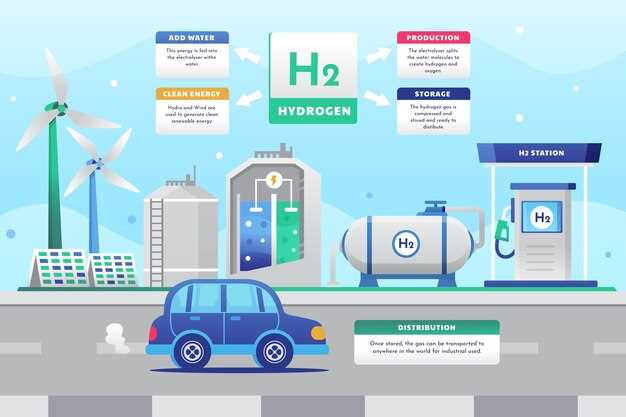
Toyota has long been at the forefront of automotive innovation, and its commitment to sustainable mobility is exemplified by its range of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). These cars harness the potential of hydrogen as a clean energy source, converting it into electricity to power electric motors. This technology not only provides an alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles but also contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting environmental sustainability.
The revolutionary hydrogen fuel cell technology utilized in Toyota’s vehicles offers significant advantages. With a quick refueling process that takes approximately the same time as conventional gasoline refueling and a driving range comparable to that of internal combustion engine cars, hydrogen cars present a practical solution for eco-conscious consumers. Moreover, the only byproduct of this process is water vapor, highlighting the potential of hydrogen as a clean energy source.
In addition to the technical aspects, Toyota’s approach emphasizes the importance of building a robust hydrogen infrastructure to support the widespread adoption of these vehicles. As the company continues to invest in research and development, insights gained from their experience contribute not only to the advancement of hydrogen technology but also to the overall growth of a sustainable automotive industry.
Understanding the Technology Behind Toyota Mirai
The Toyota Mirai represents a significant advancement in automotive technology, specifically in the field of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. It combines innovative engineering with sustainable energy solutions. Here is an overview of the key technologies that underpin the performance and efficiency of the Mirai.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell System: The core of the Mirai’s technology is its hydrogen fuel cell stack, which converts hydrogen into electricity. This process involves an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing only water vapor as a byproduct.
- Hydrogen Storage: The Mirai is equipped with high-pressure hydrogen tanks made from advanced composite materials. These tanks safely store hydrogen at 700 bar, allowing for extended driving ranges.
- Electric Drive Motor: The electricity generated in the fuel cell powers an electric motor. This motor drives the wheels, offering a smooth and efficient acceleration, typical of electric vehicles.
The following factors contribute to the overall efficiency and appeal of the Toyota Mirai:
- Range: The Toyota Mirai boasts a driving range of approximately 400 miles on a single tank of hydrogen, making it suitable for long-distance travel.
- Refueling Time: Refueling the Mirai takes only about 5 minutes, comparable to traditional gasoline refueling, which enhances its practicality for consumers.
- Environmental Impact: By utilizing hydrogen as a fuel source, the Mirai contributes to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
In summary, the Toyota Mirai leverages cutting-edge fuel cell technology to deliver a compelling alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. Its innovative systems not only provide performance and efficiency but also champion environmental stewardship, heralding a new era of clean transportation.
Benefits and Challenges of Owning a Hydrogen Car

Owning a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle (FCV) like those offered by Toyota presents a unique set of advantages and challenges. Understanding these factors is crucial for potential owners looking to transition to hydrogen technology.
Benefits:
Environmental Impact: Hydrogen cars produce only water vapor as a byproduct, making them an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. This significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants.
Refueling Convenience: Refueling a hydrogen car typically takes about the same time as refilling a gasoline vehicle–approximately 3 to 5 minutes. In contrast to recharging electric vehicles, hydrogen refueling presents a more time-efficient option for drivers on the go.
Driving Range: Hydrogen vehicles, such as those from Toyota, often offer a longer driving range compared to battery electric vehicles. Many models can travel over 300 miles on a single tank of hydrogen, which alleviates concerns about range anxiety.
Performance: Hydrogen cars deliver smooth and quiet operation, along with instant torque, providing an enjoyable driving experience. The performance of these vehicles rivals that of traditional internal combustion engines.
Challenges:
Infrastructure Limitations: One of the primary challenges of owning a hydrogen vehicle is the limited availability of refueling stations. While the infrastructure is gradually expanding, it is still significantly less developed than the networks for electric vehicle charging stations.
Cost: Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles typically come at a higher initial purchase price compared to their gasoline or electric counterparts. Additionally, the cost of hydrogen fuel can be variable, impacting long-term ownership expenses.
Public Perception: Many consumers are still unfamiliar with hydrogen technology, leading to misconceptions and hesitancy in adoption. Greater awareness and education are needed to promote the benefits and viability of hydrogen cars.
Overall, while owning a hydrogen vehicle like those produced by Toyota offers notable benefits such as environmental sustainability and convenience, potential owners must also consider the existing challenges in infrastructure, cost, and public perception. Balancing these factors will be key to the future growth and acceptance of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
Fueling Infrastructure and Future Developments for Hydrogen Vehicles
The success of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, such as the Toyota Mirai, heavily depends on the availability and development of a robust fueling infrastructure. Currently, the network of hydrogen refueling stations is limited compared to traditional fuel stations. However, numerous initiatives are underway globally to expand this infrastructure, making hydrogen-powered cars more accessible to consumers.
Many countries are recognizing the potential of hydrogen as a clean energy source and are investing in the construction of new refueling stations. For example, the United States and Japan have set ambitious targets for the number of hydrogen stations by the mid-2020s, aiming to create a comprehensive network that supports increased adoption of vehicles like the Toyota Mirai.
Future developments in hydrogen fueling infrastructure are likely to focus on several key areas. Firstly, advancements in hydrogen production, particularly green hydrogen derived from renewable sources, will enhance the sustainability of fueling operations. Secondly, innovations in storage and distribution methods will improve the efficiency and safety of transporting hydrogen.
Toyota is actively involved in these advancements and collaborates with various stakeholders, including governments and private sectors, to promote the growth of the hydrogen economy. Their vision includes not only expanding the network of refueling stations but also integrating hydrogen production within local energy systems to reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
Another crucial aspect of future developments is the consumer acceptance of hydrogen cars. As infrastructure improves, public awareness campaigns and education about the benefits of hydrogen vehicles will play a significant role in accelerating adoption rates. The availability of models like the Mirai will serve as a catalyst for interest as consumers become more familiar with the technology and its advantages, such as zero emissions and long driving ranges.
In conclusion, the future of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles hinges on establishing a comprehensive fueling infrastructure and fostering technological advancements. With continued investment and innovation, vehicles like the Toyota Mirai can become a sustainable and mainstream choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
